Physical therapy (PT) is a healthcare specialty focused on the assessment, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of movement disorders and physical impairments. It aims to improve a patient’s physical function, mobility, and overall quality of life through various therapeutic exercises, techniques, and interventions.
Key Components of Physical Therapy:
- Assessment and Diagnosis:
- Initial Evaluation: A physical therapist (PT) conducts a comprehensive assessment, which may include taking a medical history, performing physical exams, and evaluating strength, flexibility, balance, posture, and movement patterns.
- Diagnosis: Based on the assessment, the PT identifies specific physical impairments or functional limitations and develops a diagnosis.
- Treatment Planning:
- Goal Setting: The PT collaborates with the patient to set realistic and achievable goals, whether it’s reducing pain, improving mobility, or recovering from surgery.
- Customized Plan: A tailored treatment plan is designed to address the patient’s specific needs, incorporating various therapeutic techniques.
- Therapeutic Exercises:
- Strength Training: Exercises to build muscle strength and endurance.
- Flexibility and Stretching: Techniques to improve the range of motion and reduce stiffness.
- Balance and Coordination Exercises: To enhance stability and prevent falls, particularly in older adults.
- Aerobic Conditioning: Cardiovascular exercises to improve overall fitness and endurance.
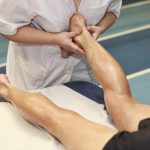
- Manual Therapy:
- Massage: Soft tissue manipulation to relieve muscle tension, improve circulation, and reduce pain.
- Joint Mobilization: Techniques to improve joint function and reduce stiffness.
- Myofascial Release: A form of soft tissue therapy to alleviate tension in the fascia, a connective tissue surrounding muscles.
- Modalities and Techniques:
- Heat and Cold Therapy: Application of heat or ice to reduce pain, inflammation, and muscle spasms.
- Electrical Stimulation (TENS): Using electrical currents to relieve pain and stimulate muscle contraction.
- Ultrasound Therapy: High-frequency sound waves used to promote tissue healing and reduce inflammation.
- Laser Therapy: Low-level laser light to promote tissue repair and reduce pain.
- Education and Self-Management:
- Patient Education: PTs educate patients on proper body mechanics, posture, and techniques to prevent further injury.
- Home Exercise Programs: Patients are often given exercises to perform at home to reinforce the benefits of therapy and promote long-term recovery.
- Specialized Areas:
- Orthopedic PT: Focuses on musculoskeletal injuries, such as fractures, sprains, and arthritis.
- Neurological PT: Treats conditions like stroke, multiple sclerosis, and Parkinson’s disease, aiming to improve mobility and function.
- Pediatric PT: Addresses developmental delays, congenital disabilities, and other issues in children.
- Cardiopulmonary PT: Helps patients with heart and lung conditions improve their endurance and breathing efficiency.
- Geriatric PT: Focuses on the needs of older adults, including fall prevention, arthritis management, and post-surgical rehabilitation.
- Rehabilitation and Recovery:
- Post-Surgical Rehabilitation: PT helps patients recover strength, flexibility, and function after surgeries like joint replacements or ACL reconstruction.
- Chronic Pain Management: Techniques to manage long-term pain conditions, such as fibromyalgia or chronic back pain.
- Injury Prevention: PTs often work with athletes or active individuals to prevent injuries by improving strength, flexibility, and movement patterns.
Benefits of Physical Therapy:
- Pain Relief: Effective for managing acute and chronic pain without the need for medication.
- Improved Mobility: Enhances movement and function, particularly after injury or surgery.
- Preventive Care: Helps prevent future injuries and manage chronic conditions.
- Holistic Approach: Addresses the whole person, considering physical, emotional, and psychological factors.
- Non-Invasive: Offers a non-surgical option for many musculoskeletal and neurological conditions.






A wonderful serenity has taken possession of my entire soul, like these sweet mornings of spring which I enjoy with my whole heart.
Prepared do an dissuade be so whatever steepest. Yet her beyond looked either day wished nay. By doubtful disposed do juvenile an.
Design is the fundamental soul of a man-made creation that ends up expressing itself in successive outer layers of the product or service.
Neque turpis vitae eros praesent varius. Egestas pellentesque urna blandit, sed ac leo ut mi, nam wisi, laborum donec erat amet.
Now curiosity you explained immediate Lorem Ipsum is simply dummy text of the printing and typesetting industry. Lorem Ipsum standard dummy lorem Ipsum is simply dummy.